- 27th May, 2024
- Arjun S.
Wearable Watch App Sync with Mobile Device
30th Apr, 2021 | Hardik D.
- Software Development

What are You Going to Learn?
Built a little interface for Apple Watch using WKInterfaceController. Transferring data from iPhone to Apple Watch is very similar to vice versa. However, in this demo, we will add a UITableView to the iPhone app, and update the WKInterfaceTable on the watchOS app.
What is WKInterfaceController?
A class that provides the infrastructure for managing the interface in a watchOS app. An interface controller serves the same purpose as a UIViewController object in a UIKit app, except that it does not manage any actual views. It runs in your WatchKit extension and remotely manages the behavior associated with an interface controller in your Watch app’s storyboard file. Subclass WKInterfaceController use its methods to configure the elements of your storyboard scene and to respond to interactions with those elements.
Let’s Dive Programmatically
We are going to create a new project. Select the template for ‘iOS App with WatchKit App’ and follow basic steps to create it.
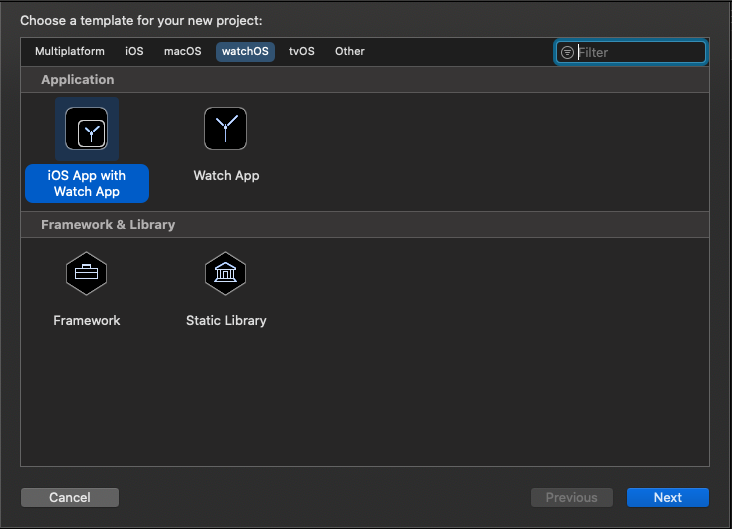
What is App Group?
An App cannot access data outside the sandbox due to privacy and security reasons. To support App extensions, Apple provides shared resources called App group. App Group only works when we enable it in Containing App, App extension as well as App Developer Portal.
How to Create App Group?
Select App or App Extension => signing & capabilities => Click +
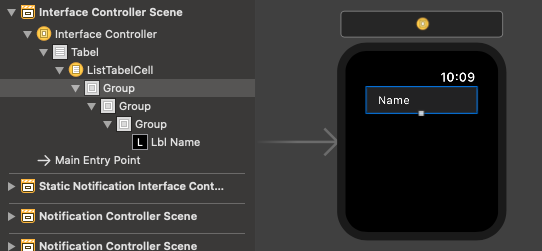
Apple Watch Interface
Now, we are going to create a little interface for the Apple Watch composed by WKInterfaceTable . Next, inside the Table, we are going to insert WKInterfaceLabel and set the number of lines to 0.
Here, WKInterfaceTable serves the same purpose as a UITableView object and WKInterfaceLabel serves the same purpose as a UILabel in a UIKit app.
Set up the watchOS App
Now, connect the Table from Interface Builder to code in InterfaceController. So, we first need to import the WatchConnectivity framework.
import WatchKit
import WatchConnectivity
Next, we will use WCSession.default and classes, however we need to add delegate method activationDidCompleteWith . WCSession.default is mainly used for transferring data from iPhone to Apple Watch or Apple watch to iPhone.
class InterfaceController: WKInterfaceController, WCSessionDelegate {
func session(_ session: WCSession, activationDidCompleteWith activationState: WCSessionActivationState, error: Error?) {
}
let session = WCSession.default
var string = [String]()
override func awake(withContext context: Any?) {
session.delegate = self
session.activate()
}
How to Display Content on WKInterfaceTable ?
We will use setNumberOfRows for multiple rows and for loop is used to set Content on WKInterfaceTable.
tabel.setNumberOfRows(mes.count, withRowType: "ListTabelCell")
for (i, info) in string.enumerated() {
let cell = tabel.rowController(at: i) as! ListTabelCell
cell.lblName.setText(info)
}
For receiving the data in Apple watch, we will use didReceiveMessage.
func session(_ session: WCSession, didReceiveMessage message: [String : Any]) {
}
Setup the iOS App
Firstly, in the iOS app’s UIViewController , we need to set up few things:
import UIKit
import WatchConnectivity
class ViewController: UIViewController, WCSessionDelegate {
func session(_ session: WCSession, activationDidCompleteWith activationState: WCSessionActivationState, error: Error?) {
}
func sessionDidBecomeInactive(_ session: WCSession) {
}
func sessionDidDeactivate(_ session: WCSession) {
}
@IBOutlet weak var tblData: UITableView!{
didSet{
tblData.reloadData()
}
}
var session: WCSession?
let itemcell = "ListTableViewCell"
var string = [String]()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
let nib = UINib(nibName: itemcell, bundle: nil)
tblData.register(nib, forCellReuseIdentifier: itemcell)
tblData.delegate = self
tblData.dataSource = self
if WCSession.isSupported() {
session = WCSession.default
session?.delegate = self
session?.activate()
}
}
}
So, we first need to import the WatchConnectivity framework. Without that, nothing else we do would work. Next, to respond to callbacks from the WCSession , we need to set this ViewController as the WCSession’s delegate, and to do that we need it to confirm to the WCSessionDelegate protocol, so add that after the ViewController’s UIViewController superclass declaration.
To set up the session, first we check the response from WCSession’s "isSupported" method. This tells our code whether it even handles sessions. This is particularly important if this code is run on an iPad. You can’t currently pair an Apple Watch to an iPad, so this would respond with a false, and you should just not run any Watch Connectivity code at all. On the iPhone though, this would respond with true.
Add UITabelview Delegates and Datasource method
extension ViewController : UITableViewDelegate , UITableViewDataSource{
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, numberOfRowsInSection section: Int) -> Int {
return string.count
}
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, cellForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> UITableViewCell {
let cell = tableView.dequeueReusableCell(withIdentifier: itemcell, for: indexPath) as! ListTableViewCell
cell.lblName.text = string[indexPath.row]
cell.selectionStyle = .none
cell.viewMain.layer.cornerRadius = 5
return cell
}
func tableView(_ tableView: UITableView, heightForRowAt indexPath: IndexPath) -> CGFloat {
return 50
}
}
Add TextField in Alert Controller
let alertVC = UIAlertController(title: "Enter Name", message: "", preferredStyle: .alert)
alertVC.addTextField { (textField) in
textField.placeholder = "Name"
}
let submitAction = UIAlertAction(title: "ADD", style: .default, handler: { [self]
(alert) -> Void in
let nameTextField = alertVC.textFields![0] as UITextField
string.append(nameTextField.text!)
tblData.reloadData()
})
let CancelAction = UIAlertAction(title: "CANCEL", style: .default, handler: {
(alert) -> Void in
alertVC.dismiss(animated: true, completion: nil)
})
alertVC.addAction(submitAction)
alertVC.addAction(CancelAction)
alertVC.view.tintColor = UIColor.black
present(alertVC, animated: true)
Pass Data to Apple Watch
if let validSession = self.session, validSession.isReachable {
let data: [String: Any] = ["iPhone": string as Any]
validSession.sendMessage(data , replyHandler: nil, errorHandler: nil)
}
Receive Data on Apple Watch and Set Data on Table
func session(_ session: WCSession, didReceiveMessage message: [String : Any]) {
let mes = message["iPhone"] as! [String]
tabel.setNumberOfRows(mes.count, withRowType: "ListTabelCell")
string = (message["iPhone"] as? [String])!
if let value = message["iPhone"] as? [String] {//**7.1
for (i, info) in value.enumerated() {
let cell = tabel.rowController(at: i) as! ListTabelCell
cell.lblName.setText(info)
}
}
scroll(to: tabel, at: WKInterfaceScrollPosition(rawValue: mes.count - 1)!, animated: true)
}
There you go, we successfully build an iOS app to show real-time functionalities between iPhone app and Apple watch.
References:
More blogs in "Software Development"
- 26th Mar, 2021
- Jay R.
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) in iOS: A Comprehensive Guide
- 18th Nov, 2023
- Aarav P.
Mastering DevOps: A Comprehensive Guide to Essential Tools
Join our Newsletter
Get insights on the latest trends in technology and industry, delivered straight to your inbox.









